Carrier Ethernet and Networking Services
- Technology Development of Carrier Ethernet
As IP technology is gradually replacing traditional technologies, the trend of a full IP network is irresistible. Enjoying the innate advantage of convergence with IP, Ethernet gradually goes beyond the applications within Local Area Networks (LAN) by virtue of its advantages such as better price-performance ratio per Mb bandwidth, simple management, flexible service loading, and low cost, and has become one of the leading networking technologies for Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs).
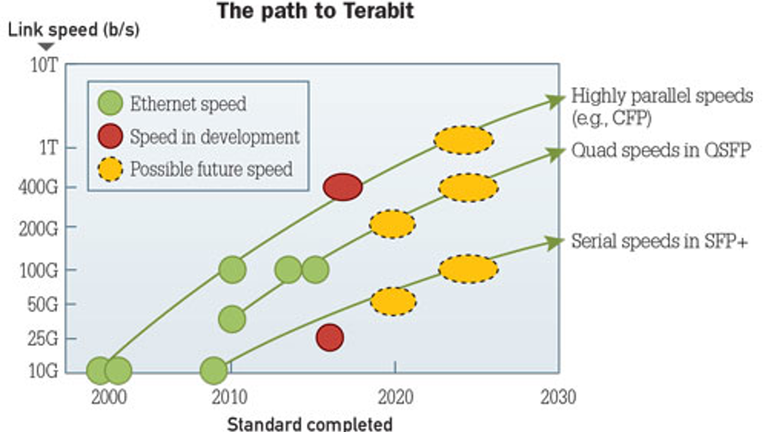
On the one hand, the development of Ethernet technologies is reflected by the rate improvement from 10 Mb/s to 10 Gb/s; on the other hand, it is reflected by enhanced performance. New technologies for Quality of Service (QoS) guarantee, reliability and manageability are constantly emerging.
- Emerging Business Trends Shaping The Future
A number of business trends have emerged that are changing the traditional nature of telecom products and services and driving new demand curves. For example, the maturation of virtualisation and cloud-based applications is driving significant changes in user behaviour and network resource utilisation.
Since virtualisation is a demand trend that is shifting IT resources from the Local Area Network (LAN) into an operator or application service provider’s network, it stresses the network to adapt and scale quickly while ensuring quality and performance, particularly for those mission critical applications for which the enterprise user is now trusting someone else to support.
Service providers are left with no choice but to evolve their business model to one that more effectively manages the demand for new services and network traffic distribution as well as bandwidth growth requirements, all of which can be addressed with Carrier Ethernet technology.
Service providers use Carrier Ethernet to:
- Interconnect business offices or data centers. Metro Ethernet can connect two sites or hundreds of sites.
- Connect residential subscribers or businesses to the Internet.
- Provide connectivity to public or private cloud data centers.
- Provide wholesale mobile backhaul services.
- Provide multicast delivery used by business customers for video conferencing, and used by residential subscribers for IPTV and video applications.
- Metro Carrier Ethernet (CE) Technology
When applied into operators’ networks, metro Ethernet technology has to meet the carrier-grade requirements. Currently, common Ethernet aggregation networks adopted by operators in broadband access networks of MANs cannot satisfy the requirements of NGN, IPTV and other high-quality services. Specifically, it cannot meet the requirements for reliability protection, and cannot provide good service management and network operation and maintenance owing to its poor Operation, Administration and Maintenance (OAM) capabilities; moreover, it is difficult to establish an end-to-end secured channel.
In order to distinguish from traditional Ethernet applications and reflect the carrier-grade features, the telecom industry has proposed the concept of Carrier Ethernet (CE), which refers to metro Ethernet with scalability, QoS, reliability, security and manageability that can be used in operators’ networks. Today, it has become one important task for operators to adopt CE networking technology to optimize their IP MANs for implementing their multi-service bearing capabilities.
Metro Ethernet is an Ethernet transport network that provides point-to-point or multipoint connectivity services over a metropolitan area network (MAN). Ethernet originated as a LAN technology, and became a replacement for low-speed WAN technologies.
- The Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF)
Communication industry came together to leverage benefits of Ethernet technology by defining and standardizing Ethernet services, making them reliable and scalable and specifying QoS and service management. This step was essential to make Ethernet-based services carrier grade.
The Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) laid the foundations for Carrier Ethernet by establishing five areas which distinguished it from LAN Ethernet. These are: Standardised Services, Scalability, Reliability, Quality of Service (QoS) and Service Management. These attributes provide carrier-class capabilities to transform traditional LAN Ethernet into a technology suitable for deployment in service provider Metro and Wide Area Networks (MANs and WANs). Providers can use Carrier Ethernet-based business services to deliver these capabilities while minimising the cost of delivery, compared with other technologies.
- Carrier Ethernet Network Service Types
The MEF also defined three key service types associated with Carrier Ethernet: E-Line services to provide a secure, point-to-point connection between two customer locations, E-LAN services to enable an extension of a business LAN to multiple locations and the emerging E-Tree service type supports multicast services, such as business IP television (IPTV).
- UNI: User Network Interface. In telecommunications, an UNI is a demarcation point between the responsibility of the service provider and the responsibility of the subscriber. This is distinct from a Network to Network Interface (NNI) that defines a similar interface between provider networks.
- POP (Point Of Presence) is the local access point for an Internet service provider (ISP). A PoP typically houses servers, routers, network switches, multiplexers, and other network interface equipment, and is typically located in a data center. ISPs typically have multiple PoPs. PoPs are often located at Internet exchange points and colocation centres.
[More to come ...]