3GPP and LTE Evolution To 5G and Beyond
- [5G Evolution To 6G - Rohde & Schwarz]
5G - Powering the New Digital Economy
- Overview
The evolution from 3GPP (the 3rd Generation Partnership Project) LTE to 5G and beyond involves a continuous process of improvement through new 3GPP releases, moving from the Evolved Packet System (EPS) to the new 5G Core Network (5GC).
While 5G introduces new technologies like the NR (New Radio) air interface, it also builds on and enhances LTE with features like LTE-Advanced Pro, which serves as a bridge to 5G, and continues to evolve with releases like 16, 17, and the upcoming 5G-Advanced and 6G.
A. LTE to 5G evolution:
- Incremental improvements: The transition is as much an evolution of LTE as it is a revolution, with many 5G features built upon LTE technology through various 3GPP releases (8-14).
- LTE-Advanced Pro: This is the official term for the set of advanced LTE technologies that serves as a bridge to 5G, with features developed in releases 13 and 14.
- Phase 1 of 5G: Initial 5G deployments (around 2020) were based on a combination of new 5G New Radio (NR) features and the existing, enhanced LTE network.
- Backward compatibility: 5G was designed to integrate with the existing LTE ecosystem to maximize the benefits of the established infrastructure and economies of scale.
B. 5G and beyond:
1. 5G New Radio (NR): This new air interface is a core component of 5G, designed to handle a wider range of services beyond just mobile broadband.
2. 5G Core (5GC): 5G introduces a new, cloud-native core network architecture, though initial deployments can still use the older EPC (EPS).
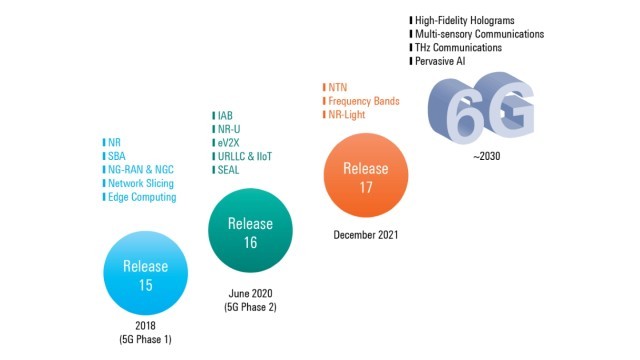
3. Release 15 and beyond:
- Release 15: Incorporated the initial set of NR features for 5G, along with control plane steering of roaming.
- Release 16: Included features for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC).
- Release 17: Introduced support for verticals like asset tracking, critical medical applications, and the Reduced Capability (RedCap) IoT standard.
4. 5G-Advanced (Release 18 and beyond):
- This is the next phase of 5G development, focusing on enhanced capabilities like extended reality (XR), integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), and AI/ML integration into networks.
- It is also laying the groundwork for the eventual development of 6G.
Please refer to the following for more information:
- Wikipedia: 5G
- Wikipedia: 6G
- Wikipedia: Next Generation Mobile Networks
- Wikipedia: List of Wireless Network Technologies
- The Key Roles of 3GPP and the ITU for the Future Mobile Systems
3GPP develops the technical standards (like 5G NR) for mobile networks, building on requirements from the ITU, ensuring global interoperability, and that 5G coexists with older 2G/3G/4G systems due to deployment costs and operator investment, with 2G/3G phasing out for 5G space, showing 3GPP's crucial role in evolving mobile comms through sequential "Releases".
In essence: The ITU defines what is needed (next-gen requirements), and 3GPP defines how to build it (the technical standards).
The key roles of 3GPP and the ITU:
- 3GPP's Role: The Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) creates detailed technical specifications (standards) for mobile technologies like 5G.
- ITU's Role: The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) sets the high-level requirements and timelines for new mobile generations (IMT-2020 for 5G).
- Coexistence: 5G must coexist with 4G (LTE), 3G, and 2G because new tech deployment takes time and investment, allowing operators to maximize existing infrastructure while transitioning.
- Phased Rollout: 2G and 3G networks are being retired to free up spectrum and resources for 5G.
- 3GPP Releases: Progress is measured in numbered Releases (e.g., Release 15 for initial 5G, Release 16 for enhancements), with work on future releases happening in parallel.
- 3GPP Specification Release Numbers
3GPP releases organize mobile tech standards (GSM, UMTS, LTE, 5G) into numbered versions (e.g., Release 99, Release 15 for 5G, Release 18/19/20 for 5G-Advanced), progressing from early GSM phases to current 5G evolution, with each release adding features and enhancements, ensuring a structured, continuous update cycle for global mobile networks.
1. Key Release Milestones & Features:
- Phase 1 & 2: Early GSM standards.
- Release 99 (R99): Introduced the first 3G (UMTS/WCDMA) networks.
- Release 8 (R8): First LTE (4G) release, bringing an all-IP network and OFDM radio.
- Release 10 (R10): LTE-Advanced, meeting 4G IMT-Advanced criteria.
- Release 13 (R13): LTE-Advanced Pro, incorporating LTE in unlicensed spectrum.
- Release 15 (R15): The foundational release for 5G New Radio (NR).
- Release 16 (R16): Further 5G enhancements (NR Phase 2).
- Release 18 (R18): Began the "5G-Advanced" era, integrating machine learning.
- Release 19 (R19) & Release 20 (R20): Continued 5G-Advanced evolution, focusing on AI, IoT, and sensing.
2. Release Structure:
- Phases: Early GSM (Phase 1, 2).
- Year-Based: After R99, some releases used years (e.g., R2000 for Release 4).
- Numbered Releases: Standardized numbering (R99, R15, R18, etc.) for modern generations.
3. Purpose:
- Organize new features for GSM, UMTS, LTE, and 5G/6G.
- Provide stable platforms for implementation with continuous upgrades.
- LTE-Advanced
LTE-Advanced (LTE-A or 4G+) is a major upgrade to the standard 4G LTE network, boosting speeds, capacity, and efficiency by using technologies like carrier aggregation (combining multiple frequency bands) and enhanced MIMO (multiple antennas), allowing for Gigabit-level peak speeds, smoother streaming, faster downloads, and better performance in crowded areas, acting as a bridge between classic 4G and 5G.
1. Key Technologies & Features:
- Carrier Aggregation (CA): Combines several LTE frequency channels to create a wider "pipe" for data, significantly increasing download and upload speeds.
- MIMO Enhancements: Uses more antennas (e.g., 4x4 or 8x8) at base stations and devices for greater data throughput.
- Coordinated Multipoint (CoMP): Allows multiple cell towers to work together to serve a single user for improved performance, notes https://inseego.com/resources/5g-glossary/what-is-lte-advanced/.
- Relay Nodes: Intelligent repeaters that extend network coverage and capacity.
- Network Enhancements: Supports heterogeneous networks with small cells (femtocells, picocells) for better coverage and capacity.
2. Benefits for Users:
- Faster Speeds: Enables smoother HD video, quicker large file downloads, and more responsive apps.
- Higher Capacity: Allows more users to have a better experience simultaneously, even in busy locations.
- Improved Coverage: Relay nodes and better network management extend reliable service.
3. Evolution:
- Developed by 3GPP as an evolution of LTE (Release 9), typically part of 3GPP Release 10 and beyond.
- It's sometimes called 4G+, LTE+, or 4.9G, bridging the gap to 5G.
- It's backward compatible, meaning LTE-A devices work on existing LTE networks.
- LTE-Advanced Pro
LTE-Advanced Pro (also known as 4.5G or 4.9G) is a significant evolution of 4G LTE, acting as a bridge to 5G by dramatically boosting speeds (Gigabit LTE), capacity, and efficiency through technologies like carrier aggregation, unlicensed spectrum use (LAA), and advanced MIMO, while also introducing features for IoT, V2X, and public safety, expanding LTE beyond smartphones to new industries.
LTE-Advanced Pro is the official term for the set of advanced LTE technologies that serves as a bridge to 5G, with features developed in releases 13 and 14.
1. Key Enhancements:
- Gigabit LTE: Achieves multi-gigabit speeds by combining many carriers and using unlicensed spectrum.
- Carrier Aggregation: Combines more frequency channels (up to 32) for greater bandwidth.
- Licensed-Assisted Access (LAA): Uses unlicensed spectrum (like Wi-Fi bands) to boost capacity.
- Massive MIMO: Uses many antennas (up to 64) to serve more users and increase capacity.
- Advanced Modulation: Uses schemes like 256 QAM for higher data density.
- IoT & V2X: Introduces features for low-power IoT devices (NB-IoT) and Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication for smart driving.
- Public Safety: Enhances mission-critical communications with features like Device-to-Device (D2D).
2. Why It Matters (The Bridge to 5G):
LTE-Advanced Pro matures many features that become foundational for 5G, extending the life and capability of existing 4G networks, providing seamless coverage and complementary services as 5G NR (New Radio) deployments begin.
LTE-Advanced Pro creates a "data superhighway" for today's demands while preparing for future 5G use cases.
- From 3GPP LTE to 5G and Beyond: A Phased Evolution
The journey from LTE to 5G and beyond is a phased evolution led by 3GPP, transitioning from the LTE-based Evolved Packet System (EPS) to the cloud-native 5G Core (5GC) and New Radio (NR), with releases like R15, R16, and the upcoming 5G-Advanced (R18+) continually adding features, bridging technologies (LTE-Advanced Pro), and paving the way towards 6G for enhanced connectivity.
This continuous standardization process ensures new features, improved performance, and support for diverse applications, from enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to massive IoT (mMTC) and ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC).
1. Key Stages & Concepts:
- LTE (4G) & EPS: The foundation, with LTE-Advanced bringing speed boosts, leading into 5G.
- 3GPP Releases: The framework for development (e.g., Release 15 for initial 5G, Release 16 for Phase 2, Release 18 for 5G-Advanced).
- 5G New Radio (NR): The new air interface for 5G, offering massive capacity and low latency.
- 5G Core (5GC): The control center for 5G, designed for flexibility, network slicing, and cloud-native functions, replacing the older EPS core.
- LTE-Advanced Pro: A "bridge" technology enhancing LTE with 5G-like capabilities, enabling smoother transitions.
- 5G-Advanced (Rel-18+): The next evolution within 5G, building on 5GC and NR for even more advanced services, moving towards 6G.
- Who Decides What 5G Is?
3GPP decides what 5G is, developing the technical specifications and standards for the technology through a collaborative, contribution-driven process involving telecommunication standards bodies, companies (like Ericsson, Verizon, Vodafone), and technical groups worldwide, with specifications released in planned "Releases" (like Release 15 for the first 5G NR) to evolve the network.
1. Who is 3GPP?
- An alliance of seven regional telecommunication standards organizations (like ETSI, ATIS, ARIB).
- Brings together these partners and numerous other industry players (like major mobile operators and equipment manufacturers) to create unified global standards for mobile networks.
2. How 3GPP Decides on 5G:
- Contribution-Driven: Companies and experts contribute proposals for new features and technologies.
- Working Groups: These contributions are developed and refined within technical specification groups and working groups.
- Release Cycles: Standards are released in organized sets, known as "Releases," with each release introducing new functionalities and improvements (e.g., Release 15 defined the first complete 5G New Radio (NR) standard).
- Open & Collaborative: The process is open, with specifications made publicly available, ensuring global consensus on the technology.
3. Key Areas of Work:
3GPP's work covers all aspects of the mobile network, including:
- Radio Access Network (RAN)
- Service and System Aspects (SAs)
- Core Network and Terminal (CT)
- The 5G Advanced: An Evolution towards 6G
5G Advanced is the next phase of 5G, enhancing current capabilities with AI, Machine Learning, and improved efficiency for new applications (like XR, IoT) while serving as a crucial foundation and stepping stone for the eventual arrival of 6G, which promises radical leaps with integrated AI, sensing, higher frequencies (THz), and immersive experiences by 2030 and beyond, bridging the gap between today's 5G and future needs.
1. What 5G Advanced brings (Building Blocks for 6G):
- AI & ML Integration: Standardized use of AI/ML for better network management, efficiency, and new services.
- Enhanced XR & Immersive Experiences: Better support for extended reality (AR/VR/MR).
- IoT Advancements: Better handling of reduced capability (RedCap) devices and low-power IoT.
- Improved Performance: Higher precision positioning, better mobility, enhanced Massive MIMO, and increased spectral efficiency.
- Sustainability: Focus on energy efficiency and greener network designs.
- Sidelink Enhancements: Better device-to-device (D2D) communication for V2X (vehicle-to-everything) and drones.
2. How it leads to 6G:
- Continuous Evolution: 5G Advanced (starting with 3GPP Release 18) builds upon 5G (Releases 15-17) and prepares for 6G (Releases 21+) through iterative standards.
- Foundation for 6G: Technologies developed in 5G Advanced, like AI integration, advanced sensing, and new device support, become core 6G features.
- Bridge: It addresses current 5G limitations and lays the groundwork for the massive technological jump 6G will deliver.
What 6G will add (Beyond 5G Advanced):
- AI-Native Networks: AI built into the core for true real-time, data-driven operation.
- Terahertz (THz) Spectrum: Utilizing much higher frequencies for extreme speeds.
- Integrated Sensing & Communication: Networks that sense the environment as well as communicate.
- Space-Aerial-Terrestrial Integration: Seamless connection across satellites, drones, and ground networks.
- Holographic Communication: Enabling truly immersive holographic interactions.
[More to come ...]