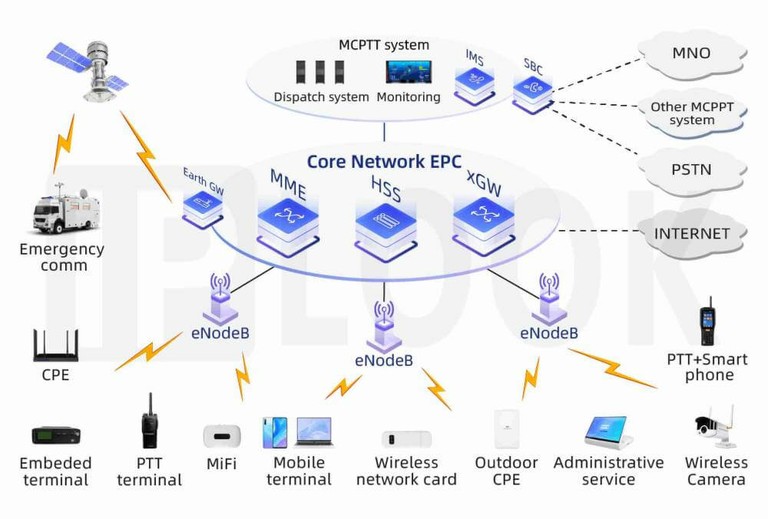
LTE EPC
- Overview
Evolved Packet Core (EPC) is a network architecture for 4G LTE that combines voice and data onto an all-IP network, replacing older circuit-switched technologies for voice.
It handles functions like authentication, session management, and setting up bearers, while also applying Quality of Service (QoS) parameters based on a subscriber's plan. The EPC's framework provides a more efficient, flat architecture that can also support other access networks like 2G, 3G, and Wi-Fi.
1. Key functions:
- Authentication: Verifies a user's identity and rights to access the network.
- Session management: Manages the state of a user's connection and data sessions.
- Bearer setup: Establishes and manages the dedicated "bearer" channels that carry data traffic.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Applies rules to prioritize and manage different types of traffic (e.g., voice vs. video) based on the user's subscription and policy.
2. Key components:
- Mobility Management Entity (MME): Manages authentication and tracks users across the network.
- Serving Gateway (S-GW): Routes and forwards user data packets between the base station and the Packet Gateway.
- Packet Gateway (P-GW): Connects the EPC to external packet data networks, like the internet, and assigns IP addresses.
- Home Subscriber Server (HSS): Stores all user subscription and profile information.
- Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF): Enforces QoS rules and policies for charging.
3. Evolution:
- The EPC is the core network for 4G LTE networks.
- It evolved into the 5G Core (5GC), which is the central component of 5G architecture and offers enhanced capabilities like network slicing and cloud-native design.
- The ability to support both 4G and 5G shows its importance as a transitional and foundational technology.
[More to come ...]