5G Network Slicing
5G Network Slicing:
The Way to Multiply the Efficiency of Internet Connectivity
- Overview
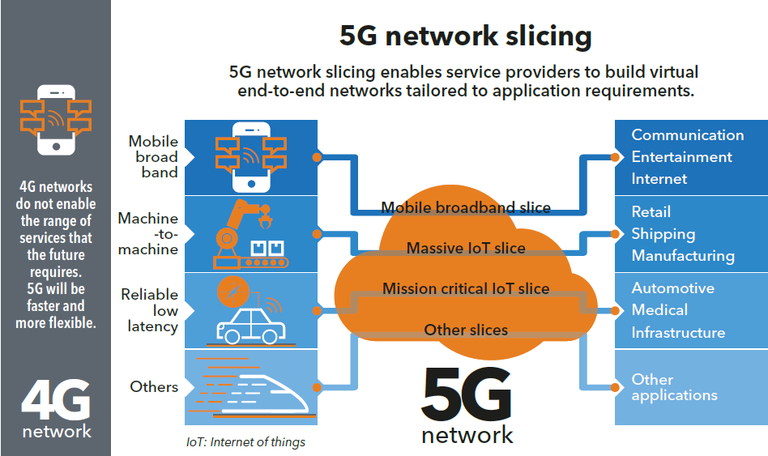
Network slicing is a 5G virtualization technology that partitions a single physical network into multiple independent, end-to-end logical networks, each customized to meet the specific requirements of different services or customers.
This allows a single 5G infrastructure to support diverse applications with varying needs for bandwidth, latency, and reliability - such as ultra-high-bandwidth video streaming and ultra-low-latency autonomous vehicle communication - all at the same time.
A. How network slicing works:
- Logical partitioning: A physical 5G network is divided into isolated "slices," which act as self-contained virtual networks.
- Customization: Each slice can be configured with its own network architecture, security settings, and quality of service (QoS) parameters tailored to a specific use case.
- End-to-end support: A slice includes all the necessary network resources, from the radio access network (RAN) to the core network, to deliver a complete, isolated service.
- Shared infrastructure: All slices run on a common physical network, eliminating the need for multiple physical networks to support different services.
B. Key features:
- Flexibility: Supports a wide range of services with diverse requirements on a single network.
- Customized performance: Guarantees specific performance levels for different applications, such as high bandwidth for video or low latency for industrial automation.
- Enhanced security: Isolates traffic between slices, preventing issues in one slice from affecting another and providing security tailored to the slice's purpose.
- New business models: Enables mobile operators to offer dedicated, high-performance network services to enterprises on a subscription basis, creating new revenue streams.
C. Examples of network slices:
- High-bandwidth slice: For high-definition video streaming, like at a sporting event, ensuring smooth, high-quality content delivery.
- Low-latency slice: For critical applications like autonomous vehicles or remote surgery, requiring near-instantaneous response times.
- Massive IoT slice: To connect a huge number of low-power devices, such as sensors in a smart city, with high connection density and potentially low data rates.
Please refer to the following for more information:
- Wikipedia: 5G Network Slicing
- A New Concept in 5G Network Slicing Technology
Network slicing is a networking architecture concept that uses a single physical network infrastructure to host multiple independent, virtualized networks.
Each "slice" operates as a self-contained virtual instance, tailored to meet the specific requirements of a particular application or service, defined by allocated network resources, topology, and service level agreement (SLA) parameters like latency, data rate, and security.
Key aspects of network slicing include:
- Virtualization Foundation: While related to older concepts like VLANs, modern network slicing fully leverages technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) to achieve its potential.
- 5G Core Component: Network slicing is fundamental to 5G deployments, extending end-to-end virtualization from the core network to the customer's device.
- Tailored Services: Different use cases receive optimized resources. For example, one slice could provide a high-reliability, data-only service for IoT smart meters, while another provides high-throughput, low-latency connectivity for an augmented reality (AR) application.
- Diverse Benefits: Operators can use slicing for internal network management, differentiating broad service classes, supporting virtual network operators, allowing customers to customize their own virtual networks, and optimizing resource management across the entire network infrastructure.
- Network Slicing Technology: A Key to 5G
Network slicing is a core 5G feature that partitions a single physical network into multiple virtual networks, each customized with dedicated resources like bandwidth and quality of service (QoS) for specific applications or users.
This allows operators to create specialized, end-to-end (E2E) networks for different needs, such as ultra-reliable services for remote surgery or massive IoT connections.
The key benefit is that it enhances operational efficiency and enables new revenue streams by providing networks on a service basis, while isolating faults within a single slice.
1. How network slicing works:
- Virtual network creation: Operators "slice" the physical 5G network into multiple, isolated virtual networks that are logically separated from one another.
- Dedicated resources: Each slice can be configured with specific characteristics, such as varying levels of network bandwidth, latency, and data speed, tailored to its use case.
- End-to-end customization: Slices are end-to-end, meaning they span across device, access, transport, and core networks, providing a complete, tailored service.
- Fault and security isolation: Because slices are isolated, security issues or performance problems in one slice do not affect others.
2. Key benefits:
- Operational efficiency: Operators can provide a range of customized services on a single physical infrastructure, reducing the need for separate networks.
- New revenue streams: It allows for the creation of "networks-as-a-service" models for different industries and applications, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities.
- Flexibility and customization: Different services with diverse requirements can be supported simultaneously, from high-bandwidth applications to ultra-low-latency critical tasks.
- Improved quality of service (QoS): By isolating traffic, network slicing ensures a more consistent user experience and stable performance, even during peak hours.
3. Critical challenges for 5G success:
- Competition with cloud providers: A major challenge is for telecom providers to effectively compete with cloud service providers for applications and data using their 5G networks.
- Network architecture and control: Operators must re-architect their networks to provide enterprise customers with control over their assets while maintaining the security and integrity of the overall infrastructure.
- Standardization and implementation: Achieving full, end-to-end network slicing across the entire industry and implementing the necessary device and infrastructure upgrades (like Standalone 5G RAN) is an ongoing process.
- 5G Network Slicing Architecture
5G network slicing is an architecture that creates multiple isolated virtual networks on top of a single physical 5G infrastructure.
This allows for the customization of each "slice" to meet the specific requirements of different applications, such as high speed for video streaming or low latency for autonomous vehicles.
Technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) are used to create and manage these independent slices, which can differ in latency, throughput, and reliability.
A. Key components and concepts:
1. Shared physical infrastructure:
- A single physical network is shared by multiple virtual, end-to-end network slices.
2. Isolated logical networks:
- Each slice acts as its own independent network, guaranteeing specific Quality of Service (QoS) for its use case and preventing performance degradation from other slices.
3. Customization:
- Slices can be tailored for diverse needs, like ultra-low latency for a remote surgery application or high bandwidth for video broadcasting.
4. Enabling technologies:
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Separates the network's control and data planes to allow for centralized management and programmability.
- Network Functions Virtualization (NFV): Virtualizes network functions, such as firewalls and routers, so they can run as software on standard hardware, making the network more flexible and cost-effective.
5. Management:
- Network slice management functions are used to create, configure, and manage the lifecycle of each slice, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently.
B. Benefits:
- Service differentiation: Operators can provide specific service levels to different customers or applications.
- New business models: Slicing enables new service offerings and supports various enterprise models.
- Cost-effectiveness: It's a more economical way to provide customized services compared to building separate physical networks for each application.
- Performance guarantee: Ensures performance for critical applications even under heavy network load by preventing resource contention.
- Applications for 5G Network Slicing
5G network slicing creates multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, enabling the simultaneous support of services with different performance needs, such as low-latency drone control and high-bandwidth mobile broadband.
This technology offers benefits like improved user experience, cost savings, and better service continuity.
However, it also introduces new security risks, as a breach in the management system could affect multiple slices.
1. Applications:
- Mobile broadband: Delivers high data speeds to mobile users.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Supports a massive number of connected devices with different requirements, such as low power consumption.
- Autonomous vehicles: Requires high reliability and ultra-low latency for real-time communication.
- Drone control: Demands high reliability and low latency for remote operation.
- Industrial automation: Enables the control of automated processes with high precision and speed.
- Remote robotic surgery: Needs ultra-low latency and high reliability for critical procedures.
- Entertainment: Provides high bandwidth for services like VR/AR and live streaming.
Benefits:
- Better user experience: Ensures specific performance levels for each service, leading to better customer satisfaction.
- Cost-effective: Allows operators to manage multiple services on the same shared physical hardware, reducing the need for dedicated physical appliances.
- Improved service continuity: Creates virtual networks on a physical infrastructure that can span multiple locations, enhancing resilience.
3. Security considerations:
- Unique security requirements: Each virtual slice has its own security needs, which adds complexity to the overall security framework.
- Centralized attack risk: A successful attack on a central 5G network management point could potentially compromise many network slices simultaneously.
[More to come ...]