SDN and SDWAN
- Software-defined Networking (SDN)
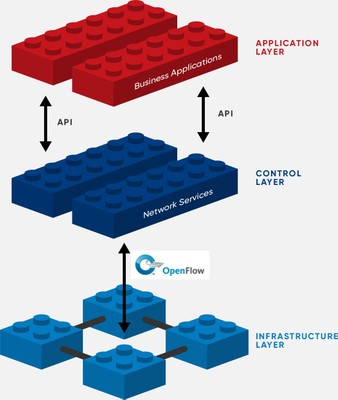
SDN architectures decouple network control and forwarding functions, enabling network control to become directly programmable and the underlying infrastructure to be abstracted from applications and network services. "SDN is the physical separation of the network control plane from the forwarding plane, and where a control plane controls several devices." - [The Open Networking Foundation (ONF)]
Software-defined networking (SDN) technology is an approach to cloud computing that facilitates network management and enables programmatically efficient network configuration in order to improve network performance and monitoring. SDN is an emerging architecture that is dynamic, manageable, cost-effective, and adaptable, making it ideal for the high-bandwidth, dynamic nature of today’s applications.
SDN is meant to address the fact that the static architecture of traditional networks is decentralized and complex while current networks require more flexibility and easy troubleshooting. SDN attempts to centralize network intelligence in one network component by disassociating the forwarding process of network packets (data plane) from the routing process (control plane). The control plane consists of one or more controllers which are considered as the brain of SDN network where the whole intelligence is incorporated. However, the intelligence centralization has its own drawbacks when it comes to security, scalability and elasticity and this is the main issue of SDN.
SDN was commonly associated with the OpenFlow protocol (for remote communication with network plane elements for the purpose of determining the path of network packetsacross network switches) since the latter's emergence in 2011. However, since 2012 OpenFlow for many companies is no longer an exclusive solution, they added proprietary techniques. These include Cisco Systems' Open Network Environment and Nicira's network virtualization platform.
- Software-defined WAN (SDWAN)
The software-defined wide-area network (SD-WAN or SDWAN) is a specific application of software-defined networking (SDN) technology applied to WAN connections such as broadband internet, 3G/4G/5G, LTE, or MPLS. It connects enterprise networks - including branch offices and data centers - over large geographic distances.
The Key advantages of the SDWAN include:
- Reducing costs with transport independence across MPLS, 3G/4G LTE, etc.
- Improving business application performance and increasing agility.
- Optimizing the user experience and efficiency for SaaS and public cloud applications.
- Simplifying operations with automation and cloud-based management.
A WAN might be used, for example, to connect branch offices to a central corporate network, or to connect data centers separated by distance. In the past, WAN connections often used technology that required special proprietary hardware. SD-WAN, on the other hand, utilizes the Internet or cloud-native private networks. SD-WAN decouples the network from the management plane and detaches the traffic management and monitoring functions from hardware. It relies on four central components:
- Edge Connectivity Abstraction
- WAN Virtualization
- Policy-Driven, Centralized Management
- Elastic Traffic Management
- 5G and SDN
802.11n is multiple input and output technology currently used in networking. 5G, or 802.11ac, is the next step in wireless technology. Right now we have 4G, but our cell phones are requiring higher bandwidths to transmit videos and gaming. 5G will provide that by annexing radio spectrum that are 1 millisecond. This will allow further development in such arenas as driverless cars. Imagine movies downloaded in a matter of seconds!
5G would be made possible by SDN and support a variety of devices and applications. One such application is virtual reality , or computer simulated, 3D images. 5G could also provide extended bandwidths to make gaming or accessing social networks more exciting using wearables, devices that communicate with the network, are mobile, and have the ability to be easily transported by wearing them.
[More to come ...]