AI and Computer Vision in Robotics
- (Robot Vision's Family Tree - ROBOTIQ)
- Overview
A robot is a machine capable of sensing and interacting with its environment. Nowadays, robots are becoming ‘smarter’ and more efficient with the help of computer science. So, artificial intelligence (AI) has played a very major role not only in increasing the comforts of humans but also by increasing industrial productivity which includes the quantitative as well as qualitative production and cost-efficiency.
AI and robotics are a powerful combination for automating tasks inside and outside of the factory setting. In recent years, AI has become an increasingly common presence in robotic solutions, introducing flexibility and learning capabilities in previously rigid applications.
While AI is still in its nascent stages, it’s been a transformative technology for some applications in the manufacturing sector, although there are many that have yet to feel the impact.
AI gives robots a computer vision to navigate, sense and calculate their reaction accordingly. Robots learn to perform their tasks from humans through machine learning which again is a part of computer programming and AI.
- The Future of Robotics
Engineers and computer scientists around the world are enhancing the perception and skills of robots. The robotics industry continues to innovate by integrating artificial intelligence, computer vision and sensing technologies.
The latest robot models are now easier to set up and program than earlier versions. Recent advances include advanced underwater exploration of ocean robots, a robot called Saul that uses ultraviolet light to fight the Ebola virus, and artificial intelligence-controlled therapy robots that improve communication between caregivers and patients.
Robots are becoming more and more human-like in both cognitive abilities and appearance. They already work alongside humans in warehouses, factories, fast food restaurants and clothing retailers.
Some robots can even perform tasks traditionally performed by humans, such as making coffee, assisting the elderly, and delivering essential items like toilet paper.
Robots are also making their way into agriculture and biomedicine, where they can harvest crops, treat disease and perform important tasks.
Despite these advances, the development of robots in various fields is not as advanced as initially predicted.
- AI's Roles in Robots
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics will change our lives, bringing excitement and uncertainty.
On the positive side, AI and robots can make daily household tasks easier, increase work efficiency, and contribute to the creation of sustainable cities. They may work alongside humans and become useful partners in creating safer and more productive environments.
However, there are challenges. Some jobs may be replaced by automation, and concerns about data privacy and rapidly evolving technology are unsettling.
While there are debates about the pros and cons, one thing is clear: AI and robotics are here to stay. We are entering a world where these technologies will become a regular part of our daily lives.
Whether this will have a positive or negative impact remains uncertain, but what is certain is that humans will need to adapt to this new reality.
AI can be categorized into different levels based on their capabilities. Depending on the use and the tasks that the robot has to perform different types of AI is used.
They are as follows:
- Weak AI: This type of AI is used to create a simulation of human thought and interaction. The robots have predefined commands and responses. However, the robots do not understand the commands they do only the work of retrieving the appropriate response when the suitable command is given. The most suitable example of this is Siri and Alexa. The AI in these devices only executes the tasks as demanded by the owner.
- Strong AI: This type of AI is used in those robots who perform their tasks on their own. They do not need any kind of supervision once they are programmed to do the task correctly. This type of AI is widely used nowadays as many of the things are becoming automated and one of the most interesting examples is self-driving cars and internet cars. This type of AI is also used in humanoid robots which can sense their environment quite well and interact with their surroundings. Also, robotic surgeons are becoming popular day by day as there is no human intervention required at all.
- Specialized AI: This type of AI is used when the robot needs to perform only specified special tasks. It is restricted only to limited tasks. This includes mainly industrial robots which perform specified and repetitive tasks like painting, tightening, etc.
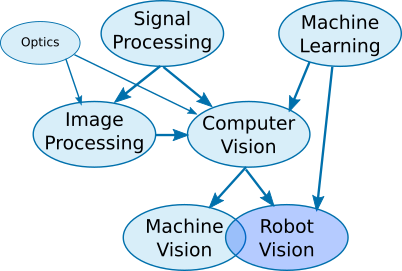
- Computer Vision' Role in Robot Vision and Machine Vision
Computer Vision (CV) is the broad field of enabling machines to "see," while Robot Vision and Machine Vision are specialized applications, with Machine Vision focusing on industrial automation (quality checks, guidance) using rule-based systems, and Robot Vision being the vision part of autonomous robots, using CV for navigation, object recognition, and complex interaction in dynamic environments. CV provides the core AI, allowing robots to interpret surroundings and make decisions, bridging simple industrial tasks (MV) with complex autonomy (RV) for applications like self-driving cars and surgical robots.
1. Computer Vision (CV):
- Definition: The overarching science of teaching computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world (images, videos).
- Focus: Deep understanding, interpretation, prediction, and complex pattern recognition.
- Applications: Face recognition, medical imaging, autonomous vehicles, AR/VR.
2. Machine Vision (MV):
- Definition: A subset of CV applied primarily in industrial settings, often rule-based for specific tasks.
- Focus: High-speed, precise, automated inspection, measurement, and guidance for manufacturing.
- Applications: Factory quality control, guiding robots on assembly lines, barcode reading, checking labels.
3. Robot Vision (RV):
- Definition: The integration of CV to give robots perception, allowing them to see and interact with their environment.
- Focus: Enabling robots for autonomous navigation, object manipulation, and complex task execution in dynamic surroundings.
- Applications: Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), robotic arms for picking/placing, surgical robots, self-driving cars.
4. Key Differences & Relationship:
- Hierarchy: CV is the parent technology; MV and RV are its children, applying CV for specific goals.
- Complexity: CV offers deeper understanding than typical MV; RV uses advanced CV for real-world interaction.
- Industrial vs. General: MV is often industrial (factory automation); RV & CV extend beyond factories to general robotics and AI.
5. How They Work Together:
- A robot uses Computer Vision algorithms to recognize a part, understand its orientation, and plan a grasp.
- This vision system (Robot Vision) might use Machine Vision techniques for precise quality checks on that part before the robot moves it.
- Together, they enable robots to perform tasks like picking varied objects from a bin, adapting to different lighting and orientations.
[More to come ...]