Future Cloud Computing and Technology
- Overview
Cloud computing is the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.
The main three types of cloud computing are public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Within these deployment models, there are four main services: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing.
The future of cloud computing will most likely represent a combination of cloud based software products and on premises compute to create a hybrid IT solution that balances the scalability, flexibility and cost optimization associated with cloud and the enhanced security and control of a private data center.
AI and machine learning (ML) are becoming increasingly integrated, leading to AI-driven cloud management and the rise of AI-as-a-service models.
Edge computing is also gaining traction, bringing data processing closer to the source, while serverless computing promises to further simplify cloud operations.
The concept of a distributed cloud is also closely tied to edge computing. This means that a single cloud provider can manage resources across multiple locations, distributing processing power while delivering a consistent experience.
Essentially, distributed systems provide the infrastructure and mechanisms for independent components to work together, and distributed computing provides ways to leverage that infrastructure to solve compute-intensive problems.
- Wikipedia: Cloud Computing
- Future Trends, Predictions, and Impacts
New technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) powered by 5G networks are driving the need for new IT architectures. Next-generation applications must not only work in mobile and web environments: they must also respond to voice, touch, wearables, and AR and VR.
Hyperplexed architecture can support a large number of widely distributed applications, different types of devices and innovative user experiences. The next generation of cloud-based platforms will support these new forms of virtualization.
Key Trends and Predictions:
- Hybrid and Multicloud: Businesses are increasingly using multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize performance.
- AI and Cloud Integration: AI and ML are being embedded into cloud services, leading to AI-driven cloud management and the rise of AI-as-a-service.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is becoming more prevalent, with data processing occurring closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless architectures are gaining popularity, enabling businesses to run code without managing servers.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing is emerging as a powerful technology, and cloud platforms are starting to offer access to quantum processors.
- Industry Clouds: Cloud providers are developing industry-specific solutions to streamline cloud migration and tailor services to specific verticals.
- Cloud-Native Applications: Containerization and Kubernetes are becoming standard for developing and deploying cloud-native applications.
- Data Privacy and Security: Emerging technologies like homomorphic encryption and confidential computing are being adopted to enhance data privacy and security in cloud environments.
- Growing Demand for Cloud Professionals: The increasing adoption of cloud computing is driving a significant demand for skilled professionals in the field.
Future Impact:
- Increased Business Agility: Cloud computing will continue to drive business innovation and enable organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Enhanced Data Management: Cloud solutions will become more sophisticated in managing and analyzing large datasets, including the use of AI and machine learning.
- Improved User Experience: Edge computing and other advancements will lead to faster, more responsive applications and a better user experience.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud technologies will continue to evolve to offer more efficient and cost-effective solutions for businesses of all sizes.
- Ubiquitous Computing: Cloud computing will become the pervasive style of computing, driving innovation across various industries and aspects of daily life.
- Cloud Computing and Its Impact on Business Growth
Businesses nowadays are seeking innovative ways to grow and accomplish their business goals. With the help of cloud computing, this business will keep on growing in the future. Cloud computing is powerful and expansive and will continue to grow in the future and provide many benefits. Cloud computing is extremely cost-effective and companies can use it for their growth. The future of cloud computing is bright and will provide benefits to both the host and the customer.
Cloud computing is a transformative technology that is enabling businesses to achieve significant growth and innovation by offering scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and access to a wide range of services, making it a key driver for business expansion in the future.
- Cost savings: Businesses can eliminate the need for expensive on-premises hardware and software, significantly reducing IT expenses and allowing them to invest in other areas like research and development.
- Scalability: Cloud services can be easily adjusted to meet changing business needs, allowing companies to add or remove resources as required without large upfront investments.
- Flexibility: Cloud platforms provide access to a variety of software applications and services, enabling businesses to quickly adapt to new market trends and customer demands.
- Accessibility: Cloud computing allows employees to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work and collaboration.
- Innovation: Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure and tools needed to develop and deploy new applications and services rapidly, enabling businesses to stay ahead of the competition.
- Improved security: Cloud providers offer robust security measures to protect sensitive data, ensuring business continuity and compliance with regulations.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud-based solutions can facilitate quick data recovery in the event of disasters or system failures, minimizing downtime and business disruption.
Overall, cloud computing is a powerful tool that empowers businesses of all sizes to grow and achieve their goals by enabling agility, innovation, and cost-efficiency.
Important considerations for businesses adopting cloud computing:
- Security concerns: Implementing proper security measures is crucial to protect sensitive data stored in the cloud.
- Data migration: Moving large amounts of data to the cloud can be a complex and time-consuming process.
- Vendor lock-in: Choosing a specific cloud provider can lead to challenges switching to another provider in the future.
- The "Hyperplexed" Future
The "hyperplexed" future of cloud computing refers to a shift towards architectures that support a large number of widely distributed applications, various device types, and innovative user experiences.
This means cloud platforms will need to handle a complex interplay of software, hardware, and user interfaces, including those enabled by technologies like 5G, AI, AR, and VR.
Hyperplexed architectures aim to simplify software development and deployment by providing native support for multicloud, edge computing, IoT, and specialized hardware.
In essence, the "hyperplexed" future of cloud computing represents a move towards a more complex, interconnected, and intelligent digital landscape. It's about creating systems that can handle the increasing demands of modern applications and user experiences, while also providing the flexibility and efficiency needed for businesses to thrive.
Key Characteristics of Hyperplexed Architectures:
- Distributed and Diverse: Applications will run across public clouds, private data centers, personal devices, and specialized hardware.
- Multimodal Interfaces: User interactions will extend beyond traditional mouse and keyboard, incorporating voice, touch, AR, VR, and other modalities.
- Integrated Technologies: Hyperplexed systems will seamlessly integrate AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies.
- Simplified Development: Tools and platforms will be designed to make it easier to develop and deploy applications across this complex landscape.
Drivers of Hyperplexed Architectures:
- 5G Networks: The increased speed and bandwidth of 5G networks enable new possibilities for real-time, distributed applications.
- Emerging Technologies: AI, AR/VR, and IoT are driving the need for more powerful and flexible computing infrastructure.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source (edge) reduces latency and improves performance for data-intensive applications.
- Software-Defined Everything: Virtualization and software-defined infrastructure are key components of hyperplexed systems.
Implications for the Future:
- Next-generation programming languages and models: New tools and frameworks will be needed to support the development of hyperplexed applications.
- Evolving roles for cloud engineers: Cloud engineers will need to adapt to the complexities of hyperplexed environments, focusing on automation, AI integration, and distributed systems management.
- More efficient and responsive systems: Hyperplexed architectures will enable businesses to operate more efficiently, respond to user needs in real-time, and adapt to changing market demands.
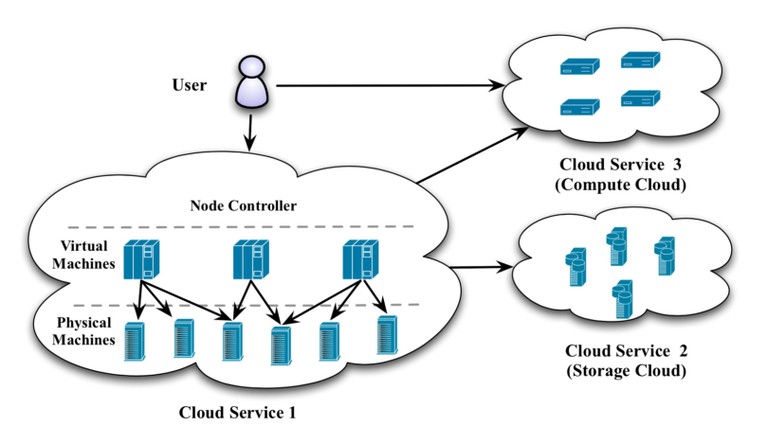
- Deployment Models and Service Models of Cloud Computing
There are 4 main types of cloud computing: private clouds, public clouds, hybrid clouds, and multiclouds. There are also 3 main types of cloud computing services: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platforms-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
Every cloud abstracts, pools, and shares scalable computing resources across a network. Every cloud type also enables cloud computing, which is the act of running workloads within that system. And every cloud is created using a unique mix of technologies, which almost always includes an operating system, some kind of management platform, and application programming interfaces (APIs). Virtualization and automation software can also be added to every kind of cloud for additional capabilities or increased efficiencies.
Cloud computing can be categorized into different deployment models and service models. Deployment models refer to how the cloud infrastructure is managed, while service models describe the type of services offered.
The main deployment models are public, private, and hybrid clouds. The primary service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Deployment Models:
- Public Cloud: Services are offered over the public internet by a third-party provider, accessible to anyone.
- Private Cloud: A cloud environment dedicated to a single organization, providing more control and security.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, allowing for the sharing of data and applications between them.
- Multicloud: Uses services from multiple public or private clouds, potentially to optimize performance, minimize costs, or avoid vendor lock-in.
- Community Cloud: Shared by several organizations with common concerns (e.g., security, compliance).
Service Models:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Provides access to fundamental computing resources like servers, storage, and networks over the internet, allowing users to manage the operating system and applications.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Offers a platform for developing, running, and managing applications, including tools, middleware, and runtime environments.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet, with the provider handling the infrastructure and maintenance.
- Serverless Computing: Allows developers to build and run applications without managing servers, focusing on code execution.
- Cloud Services and Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure is a term used to describe the components required for cloud computing, including hardware, abstract resources, storage, and network resources. Think of cloud infrastructure as the tools you need to build your cloud. In order to host services and applications in the cloud, you need cloud infrastructure.
Cloud infrastructure encompasses the hardware, software, and networking components that enable cloud computing services. It provides the foundation for delivering on-demand computing resources like servers, storage, and applications over the internet.
Abstraction techniques or processes such as virtualization are used to separate resources from physical hardware and pool them into the cloud; automation software and management tools allocate those resources and provide new environments so users can access what they need when they need it.
Essentially, it's the underlying technology that allows users to access computing power and data storage without needing to manage physical hardware themselves.
- Hardware: This includes physical servers, storage devices, networking equipment (switches, routers), and other components that form the physical infrastructure of the cloud.
- Virtualization: This technology allows resources like servers and storage to be abstracted from the physical hardware and pooled together, making them more flexible and scalable.
- Storage: Cloud storage provides a place to store data remotely, accessible over the internet.
- Networking: This component connects all the other elements and allows users to access cloud services.
- Management and Automation: Software tools automate the provisioning, management, and scaling of cloud resources, making it easier for users to access and utilize them.
- Industry Cloud Solutions
Almost every large company now utilizes public cloud resources for computing capacity, data storage, and some software (SaaS) needs. With the rapid digitization of business processes we are seeing, the popularity of public clouds (or clouds that provide enterprise "tenants" with access to public clouds) has accelerated.
However, public cloud products have recognized limitations that limit their use simply because they are general-purpose products and not optimized for the specific needs of a single industry. An industry cloud is a collection of cloud services, tools, and applications tailored to the specific needs of a single industry. While most large companies are now leveraging public cloud resources, leveraging industry clouds can unlock significant additional benefits.
Industry clouds are cloud computing solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of a particular industry. They offer pre-built applications, best practices, and data models designed with industry-specific requirements in mind. These platforms help businesses accelerate digital transformation, improve efficiency, and address industry-specific challenges.
In essence, industry clouds offer a more focused and efficient approach to cloud computing by tailoring solutions to the specific needs of different industries, leading to faster innovation, improved operations, and better business outcomes.
Key characteristics and benefits of industry clouds:
- Industry-specific solutions: They provide tailored applications, workflows, and data models that address the unique needs of various sectors like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing.
- Accelerated adoption: Industry clouds offer a more mature starting point for cloud adoption, reducing upfront investment and time to value.
- Enhanced agility and innovation: By providing pre-built solutions, industry clouds enable businesses to respond quickly to new market demands and innovate faster.
- Improved data management and security: They often include built-in features for data governance, security, and compliance with industry regulations.
- Cost optimization: Streamlined development and the use of pre-built components can lead to cost reductions.
- Integration capabilities: Industry clouds can integrate with existing systems and applications, both within and outside the industry.
Examples of industries benefiting from industry clouds:
- Financial services: Addressing KYC regulations, analyzing transaction data, and improving fraud detection.
- Healthcare: Managing patient data, optimizing care delivery, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Retail: Personalizing customer experiences, managing inventory, and optimizing supply chains.
- Manufacturing: Improving production efficiency, managing supply chains, and enabling predictive maintenance.
- Energy: Optimizing energy consumption, monitoring systems, and ensuring grid stability.
- AI in Cloud Computing
AI in cloud computing, also known as Cloud AI or AI as a Service (AIaaS), refers to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities and services within cloud environments. This allows businesses to leverage the power of AI without the need for extensive in-house infrastructure or expertise.
Cloud AI offers numerous benefits, including improved operational efficiency, enhanced scalability, and increased security.
Cloud AI is often delivered as a service (AIaaS), with providers offering pre-trained AI models, tools, and platforms that users can access over the internet.
Cloud AI Benefits:
- Automated Processes: AI algorithms can automate repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, and reduce human error in cloud management and operations.
- Resource Optimization: AI can optimize resource utilization by predicting workload demands, enabling auto-scaling, and dynamically adjusting resources based on needs.
- Enhanced Security: AI can be used for real-time threat detection, anomaly identification, and automated responses to security incidents.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud AI enables businesses to easily scale their AI capabilities up or down based on fluctuating workloads and traffic patterns.
- Innovation Acceleration: Cloud AI provides a platform for developing and deploying innovative applications like chatbots, recommendation systems, and predictive maintenance solutions.
Examples of AI in Cloud Computing:
- Cloud providers: Offer a wide range of AI services, including machine learning platforms, natural language processing, computer vision, and more.
- Businesses: Integrate cloud-based AI solutions into their operations for tasks like customer service automation, personalized recommendations, and fraud detection.
Challenges:
- Data Security: Ensuring the security and privacy of data when using cloud-based AI services is crucial.
- Latency and Bandwidth: Potential latency issues and bandwidth limitations can affect the performance of some AI applications.
- Cost Management: Organizations need to carefully manage the costs associated with cloud-based AI services.
Cloud AI Platforms:
- Major cloud providers like Google Cloud AI, Amazon Web Services (AWS) AI, and others offer comprehensive AI platforms and services.
[More to come ...]